Connection security
Configure HTTPS certificate
A custom certificate that is trusted by all client computers and contains the DNS name of the server should be configured for MyQ Central Server:
The certificate is physically stored in the “C:\ProgramData\MyQ Central Server\Cert” directory in the following files:
server.pfx – certificate with both public and private keys
server.cer – certificate with the public key
server.key – private key
Usage of wildcard certificates is discouraged, as they pose a much higher security risk when stolen.
Block unencrypted HTTP traffic
Unencrypted HTTP traffic should not be enabled in the MyQ Central Server configuration:
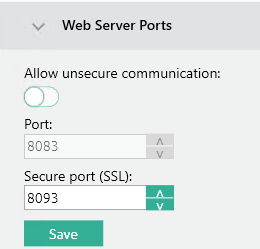
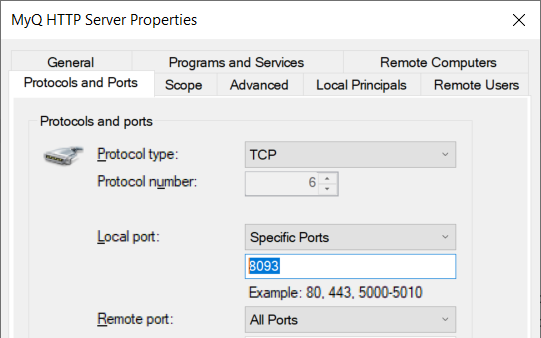
The host-based firewall should also be configured to only enable HTTPS traffic:
Encrypt database connections
If Microsoft SQL Server is used to store the MyQ database, ensure that TLS encryption is enforced through the SQL Server Configuration Manager:
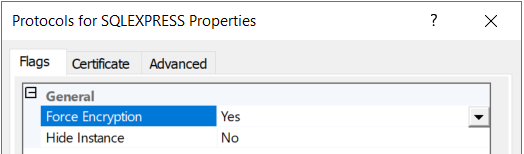
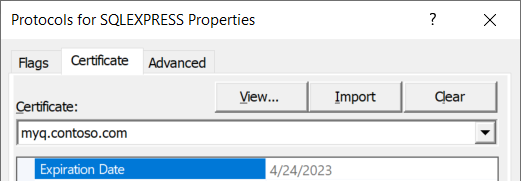
A certificate issued by a trusted CA should also be configured on the SQL Server:
Enforce encrypted LDAP traffic
If synchronization of user accounts over the LDAP protocol is used, set the connection security to SSL:
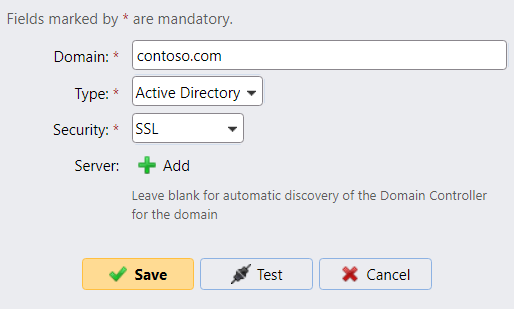
For security reasons, do not use START TLS, as it is vulnerable to MITM attacks. A certificate issued by a trusted CA must be configured on all LDAP servers (Active Directory domain controllers).
Secure SMTP traffic
If an SMTP server is configured in MyQ Central Server, enforce the usage of TLS with certificate validation:
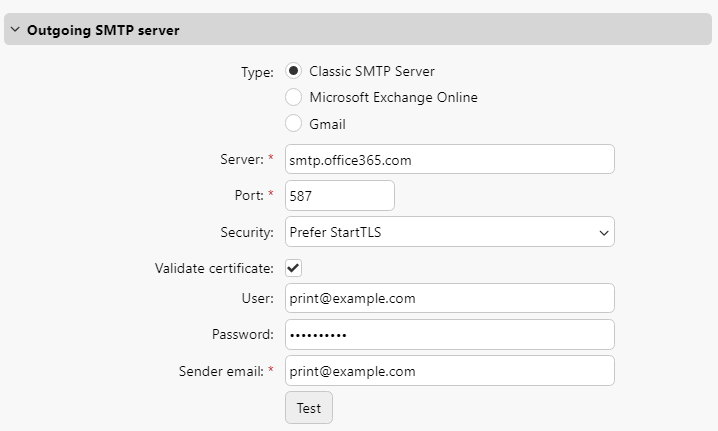
Always use FQDN
To prevent MITM attacks, strictly use fully qualified domain names in all configuration windows:
Never contact servers by only typing IP addresses or single-label names.
Secure RADIUS traffic
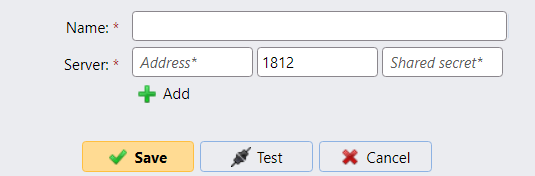
If RADIUS authentication is used, always generate strong shared secrets that are specific to the MyQ Central Server:
Protect REST API keys
When REST APIs are used, protect the client secrets from unnecessary exposure and perform periodic secret rollover:
.png)